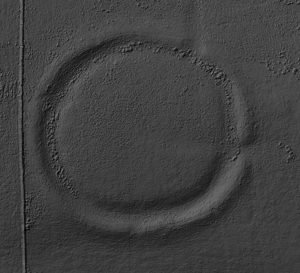
Long Meg and her Daughters is a remarkable Neolithic monument located near Penrith in Cumbria, England.
Category: Archaeology
Jul 21
Snake Iconography in the British Isles
- Filed under Archaeology, Bronze Age, Iron Age, Mace Head, Neolithic, Passage Tomb, S-curved, Snake Mound
Syncretism through the ages Syncretism, the amalgamation of different religions, cultures, or schools of thought, has its roots in the ancient world. Thoughts on Celtic Religion – Raimund, Karl To begin with, lets first look at the sources available to us: There are quite numerous sources available, contrary to Read more Hillforts: Defence or Ritual? …
Jun 27
Prehistoric mounds, cairns and boundary earthworks in Coverdale
- Filed under Archaeology, Barrow, Boundary Marker, Brigantia, Brigantia England, Bronze Age, Burial Mound, Dark Ages, Dark Ages Brigantia, Early Christian, Early Medieval, Guide, Iron Age, Landscape Archaeology, Landscape feature, Motte and Bailey, Mound, New Sites, Roman, Terraces, Visible Remains
A gazetteer of probable prehistoric mounds, cairns and boundary earthworks in Coverdale. It is not complete and is still being researched.
Jun 16
Hillforts: Defence or Ritual? – Part 1
- Filed under Archaeology, Brigantia, Brigantia England, Britain, Critical Thinking, Defensive Structures, Earthworks, Guide, Hill Fort, Univallet Hillfort, Vitrified Fort
Over the last five years Iron-Age specialists have been re-examining what British hillforts were really for. The question is no longer just “fortress or farm?” but whether many of them were built first and foremost as places of gathering, display and ritual.
- Ad Gefrin, Barry Cunliffe, battle, Bowden, Castle Dykes, Ceremony, Debate, Defence, Hill Fort, Hill of Tara, hillfort, Iron Age, Julius Caesar, Maiden Castle, McOmish, Mortimer Wheeler, Northumberland, Paulinus, Ringforts, ritual, Ritual First, tacitus, Thornborough Henges, vitrified, Yeavering Bell
- Leave comment
Castle Dykes Henge, Thoralby – North Yorkshire
- Filed under Archaeology, Brigantia, Brigantia England, Britain, Class I, Earthworks, Henge, Iron Age, Landscape feature, New Sites, Ritual Landscape
Castle dykes it is a small class one henge, 90m across, perched on the high ground up in the North Yorkshire dales. The bank survives up to 1.5 m high in places, and the ditch up to 3 m deep. Early 20th-century reports (1908) noted its intact form, and recent LiDAR-based surveys have confirmed its classic henge profile with minimal later disturbance.
Jun 11
Guide: Spoil Heaps
- Filed under Archaeology, Guide, Industrial Heritage, Landscape Archaeology, Landscape feature, Mining, Spoil Heaps
These are artificial hills made from the unwanted rock, shale and tailings that come up with coal, metal ore, stone or clay when it is being mined or quarried. Because extractive industry is both deep and long-lived, single collieries or pits can generate tens of millions of cubic metres of spoil; pushed out by locomotive, conveyor or tippler wagon and dumped in successive layers, the piles quickly become a distinctive landform.
Jun 10
Guide: Hillfort Mounds of Europe
- Filed under Archaeology, Castro Hillfort, Contour/Plateau Fort, Europe, Guide, Hidden Remains, Hill Fort, Landscape Archaeology, Landscape feature, Multivallete Hillfort, New Sites, Oppidum, Promontory fort, Slavic Gord, Univallet Hillfort, Vitrified Fort
Guide: Common Features of Iron Age Hillforts This article attempts to serve as a guide for many of the features of the hillforts found in Britain, in Read more Guide: Iron-Age minting: Ceramic Pellet-mould trays This article explores the most tangible evidence we possess for indigenous minting north of the Humber: the smashed ceramic “pellet-mould” …
Jun 10
Guide: Barrows
- Filed under Archaeobotanical, Barrow, Bell Barrow, Bowl Barrow, Bronze Age, Dark Ages, Disc Barrow, Europe, Guide, Iron Age, Landscape Archaeology, Landscape feature, Long Barrow, Neolithic, Ring Barrow, Ritual Landscape, Roman, Round Barrow, Square Barrow, Steppe Kurgan
A barrow is a mound of earth and/or stones raised over a grave or group of graves. Used from the Neolithic through to the Iron Age (roughly 4000 BCE to 500 CE), barrows were often constructed to honour elite individuals, such as tribal leaders, warriors, or chieftains. They are frequently found singly or in cemeteries known as barrow fields.
- AngloViking, Arras Culture, barrow, Barrow Timeline, Bell Barrow, Bowl Barrow, britain, Bronze Age, Burial Mound, Disc Barrow, Eastern Europe, Hallstatt, Iberian Peninsular, ireland, Iron Age, la tene, Long Barrow, Neolithc, Nordic Bronze Age, Ring Barrow, Roman, Round Barrow, ScandinaviaUkraineCentral Europe, Square Barrow, Steppe Kurgan, timeline
- Leave comment
Jun 07
Guide: SAR Doppler Tomography
- Filed under Archaeology, Geophysics, Guide, Hidden Remains, New Sites, Remote Sensing and Analysis, Reports
Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) already relies on Doppler shifts: echoes from scatterers in a side-looking radar beam have slightly different frequencies as the platform flies past, and focusing those micro-shifts yields a two-dimensional image.
- 3-D mapping, Airborne P-band, Archaeology, Back-scatter, Baseline (B⊥), Beam-forming Algorithm, Biomass, Capon, Coherence, coherent stack, Cryosphere, D-TomoSAR, differential processing, Doppler spectral cube, Forests, Height Resolution, Heritage monitoring, Infrastructure, InSAR, Interferometric SAR, Look Angle (θ), MUSIC, Penetration Depth, perpendicular baseline (B⊥), radar wavelength, RIAA, SAR, SAR Doppler Tomography, Satellite X-band stack.TerraSAR-X, Synthetic-Aperture Radar, temporal decorrelation, Tomographic SAR, TomoSAR, topography under vegetation, Voxel, Wavelength (λ)
- Leave comment
Jun 05
Guide: Classification of Henge Monuments
- Filed under Archaeology, Bronze Age, Earthworks, Henge, Iron Age, Landscape feature, Neolithic, New Sites
Archaeologists use the word “henge” for later-Neolithic and earliest Bronze-Age earthen rings whose ditch lies inside the bank, creating a deliberately bounded interior. The term itself was coined in 1932 by Kendrick; it was refined in the 1950s by Richard Atkinson, whose system still frames most discussion.
Articles
- Bronze Age
- Iron Age
- Roman
- Dark Ages
- Early Christian
- Viking
- Saxon
- Medieval
- Vitrified Fort
- Archaeology Guide
- Guide – Introduction to Critical Thinking in Archaeological Research
- Guide – Challenging Assumptions with Free Thinking
- Guide – Congruence in Archaeological Interpretation: Holistic Analysis
- Guide – Critical Thinking: Lack of Evidence Does Not Mean Evidence of Lack
- Guide – Critical Thinking: The Simple Assumption
- Guide – Applying critical thinking to historic and archaeological research
- Guide – Empathic Archaeology Introduction
- Guide – Landscape Archaeology Introduction
- Guide – What is Landscape Archaeology?
- Guide – Introduction to Glacial Archaeology
- Guide – The Flora and Fauna of Prehistoric Britain
- Guide – Landscape Archaeology: Post-Ice Age Landscape of Thornborough
- Guide – Archaeological Periods in Western Europe
- Guide – Visible Remains
- Guide – Hidden Remains
- Guide – Getting Started
- Guide – Landscape Features
- Guide – Agricultural practices through time
- Guide – Introduction to Glacial Archaeology
- Guide: In Depth – Church Doors and Windows
- Guide – Mining
- Guide – Archaeological Terms
- Guide – Glossary
- Latin Translation – Choosing the meaning of AUG
- Reports
- An introduction to Brigantian Druidry
- Brigantia during the Dark Ages
- Celtic Heads
- Finding Bardon – An Arthurian Quest
- Early Christian syncretism and how the old ones hid amongst the new religion
- Rome: The Emperors Claim to Divinity
- Syncretism through the ages
- The Border Reivers
- The Gallus Frontier – Brigantia against the Romans
- The growth of Christianity 50AD – 1100AD
- The Kingdom of Venutius
- The use of the word Lady in relation to water related structures
- The walled gardens of Brigantia
- Yorkshire’s “Sacred Vale” – The Dawn of Brigantia
- Brigantia Espania
- Iberian Peninsular
- Galicia
- Biefing – The Myth of Breogán and the Tower of Heracles
- Briefing – Galicia’s Political History and Separatist Sentiment
- Briefing – Geography and Geology of Galicia
- Briefing – Design of Galician Hillforts
- Briefing – Roman Interaction with Galicia and the Iberian Peninsula
- Church of Santa María de Cambre, Cambre near A Coruña
Categories
- Agriculture (6)
- Field Systems (1)
- ploughing (2)
- Angle (2)
- Archaeological Periods (312)
- Anglo-saxon (6)
- Bronze Age (52)
- Late Bronze Age (1)
- Dark Ages (24)
- Dark Ages Brigantia (9)
- Early Christian (37)
- Early Medieval (8)
- Georgian (9)
- Gothic (3)
- Ice Age (1)
- Iron Age (133)
- Late Iron Age (5)
- Jacobite (7)
- Medieval (61)
- Medieval Brigantia (9)
- Mesolithic (11)
- Neolithic (45)
- Early Neolithic (5)
- Norman (40)
- Palaeolithic (6)
- Roman (94)
- Saxon (9)
- Stuart (6)
- Suspect (1)
- Tudor (10)
- Undated (7)
- Viking (4)
- Archaeology (93)
- Archaeobotanical (1)
- Empathic Archaeology (11)
- Free Thinking (7)
- Battle (1)
- Brigantia (147)
- Brigantia England (134)
- Brigantia Espania (11)
- Civil Structure (6)
- Defensive Structures (45)
- Castle (5)
- Defensive Dike (2)
- Defensive Walls (1)
- Fort (20)
- Fortified Barn (1)
- Marching Camp (5)
- Motte and Bailey (6)
- Ring Work (1)
- Class A (1)
- Dialects (1)
- Earthworks (51)
- Dike (8)
- Field Systems (26)
- Enclosure (12)
- Enclosure Acts (1)
- Europe (51)
- Festivals (2)
- Finds (42)
- Altar (10)
- Amphora (1)
- Animal Remains (4)
- Auroch (1)
- Hoof marks (1)
- Antler Pick (2)
- Arrowhead (1)
- Leaf-shaped (1)
- Axe (1)
- Bone Comb (1)
- Celtic Head (8)
- Celtic Head (2)
- Clock (1)
- Curse Tablet (1)
- Flint Scatters (4)
- Gaming Pieces (1)
- Hair Braid – Ring (4)
- Human Remains (2)
- Adult (1)
- Couched Burial (1)
- Juvinile (1)
- Mace Head (1)
- S-curved (1)
- Mosaic (1)
- Polished Stone Adze (1)
- Pottery (8)
- Funerary Urns (2)
- Grooved ware (1)
- Peterborough ware (1)
- Mortlake ware (1)
- Planig‑Friedberg ware (1)
- Samian ware (2)
- Vasi a Bocca Quadrata ware (1)
- Quern Stones (1)
- Statue (1)
- Geography (16)
- Maps (7)
- Geology (13)
- Anthracite – Coal (2)
- Geomorphology (2)
- Gods (9)
- Guide (72)
- Critical Thinking (8)
- Socratic Thought (1)
- Glossary (1)
- Hidden Remains (8)
- Geophysics (5)
- LiDAR (1)
- Radiocarbon Dating (1)
- Remote Sensing and Analysis (1)
- Regional Surveys (13)
- Research Tools (4)
- Visible Remains (12)
- Air Mapping (2)
- Air Photography (2)
- Fieldwalking (2)
- Lithics (1)
- Photography (6)
- Critical Thinking (8)
- Henge (18)
- Hill Fort (61)
- Castro Hillfort (3)
- Contour/Plateau Fort (1)
- Multivallete Hillfort (1)
- Oppidum (1)
- Oppidum (1)
- Promontory fort (4)
- Slavic Gord (1)
- Univallet Hillfort (4)
- Vitrified Fort (27)
- Historic Buildings (20)
- Amphitheatre (1)
- Barn (2)
- Beacon (1)
- Broch (1)
- Coaching Inn/Hostelry (1)
- Folly (4)
- Hall (2)
- Hospital (1)
- House (1)
- Tower (7)
- Walled Garden (1)
- Industrial Heritage (9)
- Chimney (1)
- Mining (9)
- Spoil Heap (1)
- Smelting (2)
- Iron-Age (1)
- Landscape Archaeology (38)
- Glacial Archaeology (2)
- Landscape Legislation (1)
- Mining Landscape (1)
- Ritual Landscape (6)
- Landscape feature (49)
- Barrow (18)
- Bell Barrow (2)
- Bowl Barrow (1)
- Cairn (2)
- Disc Barrow (1)
- Long Barrow (5)
- Ring Barrow (1)
- Ring Cairn (1)
- Round Barrow (1)
- Square Barrow (1)
- Steppe Kurgan (1)
- Boundary Marker (2)
- Burial Mound (9)
- Ceremonial Mount (1)
- Cursus (2)
- Hill Figure (5)
- Linear Earthworks (2)
- Mound (6)
- Passage Tomb (1)
- Ring Cairn (2)
- Snake Mound (1)
- Terraces (3)
- Barrow (18)
- Leaders (33)
- Agricola (2)
- Arthur (1)
- Augustus Caesar (2)
- Breogans (3)
- Caratacus (1)
- Cnut (1)
- Julius Caesar (1)
- Petilius Cerialis (1)
- Liminal Spaces (1)
- Market (1)
- Megalithic (10)
- Rock Art (3)
- Stone alignment (1)
- Stone Circle (7)
- stone circles (1)
- Stone Row (2)
- Myth and Legend (5)
- New Sites (23)
- Publications (21)
- Biographies (2)
- Henge Capital of Britain (10)
- News (4)
- Stories of Brigantia (4)
- Walking Guides (1)
- Rabbit Warren (1)
- Religious Structures (31)
- Abbey (3)
- Church (24)
- Crosses (1)
- Memorial Planting (1)
- Priory (2)
- Religious Orders (3)
- Ritual walkway/pilrimage path (1)
- Reports (148)
- Roman Culture (11)
- Roman army (8)
- Roman baths (1)
- Roman City (1)
- Roman Gods (1)
- Mercury (1)
- Roman navy (1)
- Roman pottery (3)
- Samian ware (2)
- Roman Road (1)
- Roman Roads (2)
- Roman Villa (2)
- The Celtic World (35)
- Celtic Gods (1)
- Lugh (1)
- Celtic Industry (1)
- Celtic Life (9)
- Celtic Trade (1)
- Celtic Tribes (27)
- Celtic Gods (1)
- Trade (4)
- Minting (3)
- Coins (1)
- Spoil Heaps (2)
- Minting (3)
- Translation (7)
- Inscription (4)
- Latin (5)
- Uncategorized (24)
- Water Works (13)
Research Links
 Heritage Gateway
Heritage Gateway
Announcing: The Brigantian News!
- Roman Road to the West uncovered under Manchester Street 16 July 2025
- What might Stonehenge Mean? Dartmoor and Carnac add to the Picture 3 July 2025
- Megalithic Stone Monuments in France May Be Europe’s Oldest 1 July 2025
- Drumanagh Promontory Fort – First Ever Intact Roman Pot Found in Ireland 5 June 2025
Portable Antiquities News
An incomplete Post-Medieval copper alloy 'tombac' button (tombac being a brass alloy with high copper content and 5–20% zinc content), consisting of the upper domed plate, dating from c. AD 1600-1800. Only the domed front [...]
A thin, uneven strip of rectangular sectioned copper alloy, possibly with a small hooked terminal, however this could also just be from cutting. It may be waste material, but the patina suggests it has some [...]
A small and thin Roman nummus / minim of fourth century date. The coin is slight dished and is extremely worn, however a left-facing bust can be discerned under a magnifier, but is difficult to see [...]
A Neolithic flint arrowhead. The arrowhead is of the transverse or chisel form, being sub-triangular in plan and worked all over on both sides. The striking platform and bulb of percussion have been removed. The [...]
A flint end scraper dating to the Neolithic or Bronze Age. The scraper is made from a primary flake of dark brown flint. A cream-grey coloured cortex covers around 80% of the dorsal surface. Fine, [...]
An incomplete, copper alloy, Roman finger ring, dating to c. AD 43-300.Only the bezel and shoulders of the ring remain, the rest of the hoop is missing. The bezel has an oval-shaped, recessed profile, within which are [...]
Two fragments of an early Anglo-Saxon cruciform brooch. The fragments comprise the bow. The bow is rectangular in plan, convex, and has a moulded transverse collar at the top and the bottom. A thin moulded [...]
A medieval copper alloy buckle, circa 1200-1400. The frame is rectangular and has a narrowed bar. The sides of the frame are flat. The lip is formed of a large, circular knop. This is convex [...]
An incomplete copper alloy pin of Middle Saxon date, circa AD700-850. The pin has an undecorated, flattened globular head. A small, moulded collar is located at the top of the shank. Most of the shank [...]
An incomplete copper alloy pin of Middle Saxon date, circa AD700-850. The pin has an undecorated, flattened globular head. A small, moulded collar is located at the top of the shank. Most of the shank [...]
A possible fragment of an early Anglo-Saxon copper alloy girdle hanger. The fragment is a thin rectangular shank and probably comes from the upper part of a girdle hanger. No decoration is visible. This item [...]
A post-medieval copper alloy buckle with double oval frame. An integral central bar divides the frame and houses a copper alloy pin. The bar extends slightly beyond the edge of the frame. A moulded triangular [...]
A complete flint retouched blade of probable Mesolithic to early Neolithic date. Small secondary flake. A small amount of short, semi-parallel, abrupt retouch and a notch, which appears to be deliberate, in the centre of the [...]
A complete flint retouched flake of probable Neolithic to early Bronze Age date. Small tertiary flake. Two notches, which appear to be deliberate, along the distal edge. Narrow butt, prominent bulb. Medium patination. [...]
A complete flintworking flake of probable Neolithic to early Bronze Age date. Small secondary flake. Narrow butt, prominent bulb. Hinge fracture at distal end. No obvious signs of retouch. Unpatinated. [...]
A complete flintworking flake of probable Neolithic to early Bronze Age date. Large secondary flake. Narrow butt, prominent bulb. Hinge fracture at distal end. No obvious signs of retouch. Unpatinated. [...]
A complete flintworking flake of probable Neolithic to early Bronze Age date. Large secondary flake. Narrow butt, prominent bulb. No obvious signs of retouch. Rolling along distal edge. Unpatinated. [...]
A complete flint retouched flake of probable Neolithic to early Bronze Age date. Large secondary flake. Retouched notch in centre of left edge. Narrow butt, prominent bulb. Hinged fracture at distal end. Unpatinated. [...]
An incomplete medieval copper alloy buckle dating circa 1200-1400. The frame is D-shaped in plan with a narrowed and offset bar. The bar is mostly missing. The lip is expanded and angled diagonally upwards. The [...]
A complete flintworking flake of probable Neolithic to early Bronze Age date. Large secondary flake. Narrow butt, prominent bulb. Hinge fracture at distal end. No obvious signs of retouch. Unpatinated. [...]
Recent Articles and Site Pages
- The Story of Boltby Scar
- Swaledale
- Guide: Parliamentary-walls and the Northern Enclosures
- County Durham
- The hero archetype and Lugh
- Head One – St Michaels Church, Kirklington
- Long Meg and her Daughters standing stone and stone circle
- Cana Barn Henge
- Anciens Arsenaux Neolithic Settlement, Sion – Switzerland
- Gnaeus Julius Agricola
- Snake Iconography in the British Isles
- Wiltshire
- Liverpool Street Roman Road, Manchester
- South Street Long Barrow, Avebury
- Mamucium Roman Fort, Manchester
Locations
- Czechia (1)
- England (198)
- Bedfordshire (1)
- Cumbria (13)
- Dorset (2)
- Durham (9)
- East Yorkshire (1)
- Lancashire (7)
- North Derbyshire (8)
- North Yorkshire (118)
- Yorkshire Dales (4)
- Yorkshire Moors (1)
- Northumberland (9)
- Oxfordshire (2)
- Somerset (2)
- South Yorkshire (10)
- Staffordshire (3)
- West Yorkshire (7)
- Wiltshire (4)
- Europe (8)
- France (3)
- Germany (2)
- Global (3)
- Ireland (4)
- County Dublin (1)
- Scotland (21)
- Dumphries and Galloway (3)
- Grampian (4)
- Highlands (8)
- Perthshire (4)
- Tayside (3)
- Spain (4)
- Switzerland (1)
- Wales (4)