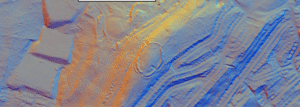
Sion lies midway along the upper Rhône Valley, an east‑west trench gouged by repeated Pleistocene glaciers and now flanked by the Pennine and Bernese Alps. The settlement area sits on the alluvial fan of the Sionne torrent, a cone of well‑sorted sands and gravels that projects onto the wider Rhône flood‑plain.
Period: Roman
Liverpool Street Roman Road, Manchester
Archaeologists have exposed a well-preserved cambered Roman road surface in Manchester’s Castlefield area (Liverpool Road/Liverpool Street reporting), astonishingly only c. 15 inches (≈38–40 cm) below modern tarmac, with an assemblage of Romano-British pottery and other small finds broadly dating its active use to the 1st–3rd centuries AD.
Mamucium Roman Fort, Manchester
Mamucium occupies a low sandstone promontory at the junction of the Rivers Medlock and Irwell. The bedrock is the Triassic Sherwood Sandstone Group, a firm, well‑drained red sandstone that gave Roman engineers a stable platform for earthworks and timber palisades, while nearby river gravels supplied road‑making aggregate.
Castro de Trona fort – Pontevedra, Spain
Castro de Trona is an oval enclosure with significant terracing to the west and a large ditch to the east. This castro (a hillfort settlement) has an accepted date of around 600 BCE. Like many others in Galicia, this castro reached its peak during the 1st and 2nd centuries CE. It measures approximately 200 metres east to west by 150 metres north to south.
Doncaster Roman Fort (Danum)
← South Yorkshire Roman Rig Defensive Works The Roman Rig is a defensive dyke built to defend against attack from the south. It runs from Sheffield, past Read more Templeborough Roman Fort – Rotherham Templeborough Roman Fort occupies a commanding position on the north bank of the River Don at Rotherham (OS grid SK Read …
Templeborough Roman Fort – Rotherham
Templeborough Roman Fort occupies a commanding position on the north bank of the River Don at Rotherham (OS grid SK 410 916), where the Magnesian Limestone ridge drops into the floodplain. Originally constructed in timber and earth in the mid–1st century AD, it was later rebuilt in stone and occupied—possibly intermittently—until the withdrawal of Roman authority in the early 5th century AD