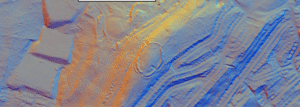
Boltby is a very important ancient site IMO. A gold “hair braid”, was found there, linking it to the Amesbury Archer, buried with two similar hair braids. This also provides a link to the founding of Stonehenge, which helps set a potential scene for a possible “zeitgeist”, of the day.
Category: Iron Age
Aug 02
The hero archetype and Lugh
At its core the “hero” is the figure who steps out of ordinary society, confronts chaos or a monster, and returns (or dies) having secured order for the group. In Jungian and comparative-myth terms it sits in the “warrior-champion” slot of the collective story-board; evolutionists would say it crystallises the survival value of decisive coalition leadership in small bands.
Castro de Trona fort – Pontevedra, Spain
Castro de Trona is an oval enclosure with significant terracing to the west and a large ditch to the east. This castro (a hillfort settlement) has an accepted date of around 600 BCE. Like many others in Galicia, this castro reached its peak during the 1st and 2nd centuries CE. It measures approximately 200 metres east to west by 150 metres north to south.
Templeborough Roman Fort – Rotherham
Templeborough Roman Fort occupies a commanding position on the north bank of the River Don at Rotherham (OS grid SK 410 916), where the Magnesian Limestone ridge drops into the floodplain. Originally constructed in timber and earth in the mid–1st century AD, it was later rebuilt in stone and occupied—possibly intermittently—until the withdrawal of Roman authority in the early 5th century AD
Great Roe Wood (Roe Wood) Enclosure – Woodhouse
Great Roe Wood (often simply called “Roe Wood”) sits on the Magnesian Limestone ridge that carries the Roman Rig between Sheffield and Doncaster, just northeast of the village of Woodhouse (OS grid SK 450 920). This ridge forms a natural corridor overlooking the Don valley, with shallow soils over limestone giving way to deeper alluvial gravels in the valley bottom.