Over the last five years Iron-Age specialists have been re-examining what British hillforts were really for. The question is no longer just “fortress or farm?” but whether many of them were built first and foremost as places of gathering, display and ritual.
Category: Europe
Bishopdale
Bishopdale lies within the northern limb of the Askrigg Block, its underlying bedrock dominated by Carboniferous limestones with intermittent shales and sandstones of the Yoredale Series. The Great Scar Limestone, a thick, massive unit formed around 330 million years ago in a shallow tropical sea, underpins the dale’s steeper scarps and cliff lines, while the thinner-bedded limestones and intervening mudstones of the Yoredale Group create the characteristic terraced flanks on which many of Bishopdale’s field systems are laid out
Kilburn White Horse
The Kilburn White Horse is a large chalk hill figure cut into the limestone of Roulston Scar, the steep escarpment that defines the western edge of the Hambleton Hills in North Yorkshire. Carved in November 1857 and measuring roughly 97 by 67 metres, it was conceived not as an ancient relic but as a deliberate Victorian creation
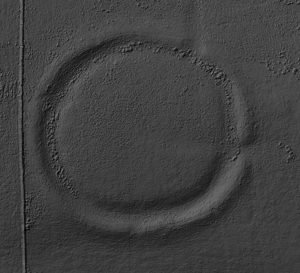
Castle Dykes Henge, Thoralby – North Yorkshire
Castle dykes it is a small class one henge, 90m across, perched on the high ground up in the North Yorkshire dales. The bank survives up to 1.5 m high in places, and the ditch up to 3 m deep. Early 20th-century reports (1908) noted its intact form, and recent LiDAR-based surveys have confirmed its classic henge profile with minimal later disturbance.
Jun 10
Guide: Hillfort Mounds of Europe
Guide: Common Features of Iron Age Hillforts This article attempts to serve as a guide for many of the features of the hillforts found in Britain, in Read more Guide: Iron-Age minting: Ceramic Pellet-mould trays This article explores the most tangible evidence we possess for indigenous minting north of the Humber: the smashed ceramic “pellet-mould” …
Drumanagh Promontory Fort – First Ever Intact Roman Pot Found in Ireland
RTE Ireland has reported that more recently they have made yet another remarkable discovery—an intact Roman pot. the first one to be uncovered on Irish soil, and providing more tantalising clues about ancient Roman-Irish interactions.
Although the Roman Empire they never reached Ireland (except, seemingly, in myth). That does not mean, that Roman influence and goods did enter Ireland, and it means that Drumanagh continues to headline as one of Irelands most tantalising archaeological sites for that same reason – exactly what were the Romans doing in Ireland?
Moulton Henge
Archaeologists now recognise a true Neolithic henge lying immediately south-west of Moulton village, roughly midway between the Swale and Dere Street. The monument is almost 200 m across, with a low earthen bank encircling an inner ditch and a central platform about 110 m wide; the ditch lies inside the bank—the classic “Class II” henge arrangement.
May 25
Brigantes Tribe
The name Brigantia represents three separate concepts: a goddess, a people, and a tribal federation. By the Roman period, the name represented a tribal federation compromising all of what would become the Roman province of Britannia Secunda, except for the Parisi territory, east of the River Derwent.