The legend of King Cnut, also known as Canute the Great, is a fascinating tale that highlights themes of humility and the limits of power. King Canute ruled over England, Denmark, and Norway in the early 11th century. He was a powerful Viking king known for his military prowess and political acumen.
The legend of King Cnut, also known as Canute the Great, is a fascinating tale that highlights themes of humility and the limits of power. King Canute ruled over England, Denmark, and Norway in the early 11th century. He was a powerful Viking king known for his military prowess and political acumen.
The historical background of King Canute (or Cnut the Great) is quite fascinating and reflects the complex political landscape of early 11th-century Europe.
Early Life and Background
Canute was born around 995 AD to Sweyn Forkbeard, the King of Denmark, and Świętosawa, a Polish princess. His lineage positioned him well for future claims to power.
Viking Expeditions: From a young age, Canute participated in Viking raids and expeditions, gaining military experience and establishing his reputation as a formidable leader.
In 1016, Canute invaded England during a period of instability following the death of King Æthelred the Unready. After a series of battles, he emerged victorious, becoming King of England. Canute faced challenges from rival claimants, particularly from the sons of Æthelred. He successfully defeated them, solidifying his rule and establishing a strong central authority.
Reign Over Multiple Kingdoms
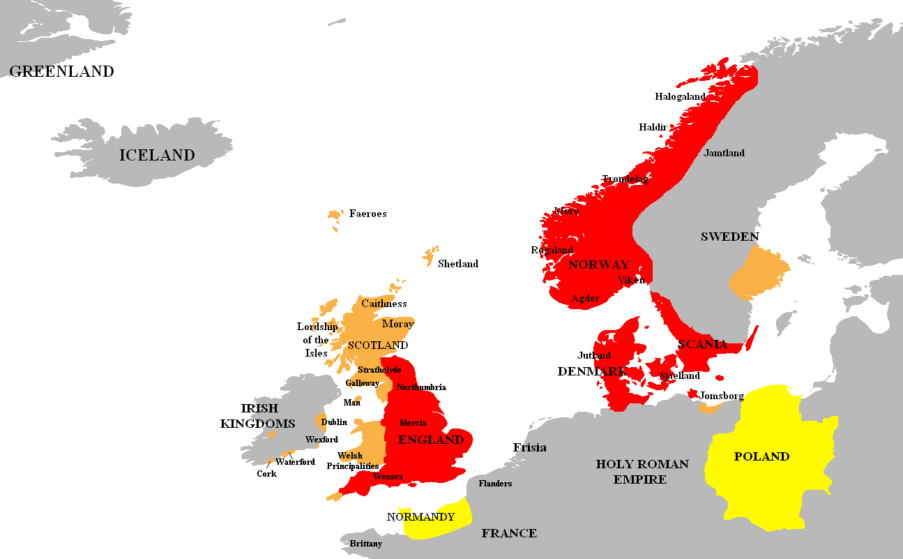
After securing England, Canute also became King of Denmark in 1018 and later claimed the throne of Norway in 1028. This led to the formation of the North Sea Empire, a significant political entity in medieval Europe.
Canute was known for his diplomatic skills. He managed to maintain peace among the diverse cultures within his realm, balancing the interests of the Anglo-Saxons, Danes, and Norwegians.
Governance and Legacy
Canute implemented various legal reforms, promoting justice and order within his kingdoms. He worked to integrate Danish and English laws, fostering a sense of unity.
He was a devout Christian and played a crucial role in promoting Christianity in Scandinavia, which helped to strengthen his rule and align his kingdoms with the broader Christian Europe. Canute’s reign is often seen as a high point of Viking influence in Europe. His ability to rule over multiple kingdoms showcased the potential for Viking leaders to transition from raiders to rulers.
King Canute’s reign was marked by military success, political savvy, and cultural integration. His legacy is not just about conquest but also about the establishment of a stable and prosperous empire that influenced the course of European history.
The King that could not Command Nature
The most famous story associated with him is the one where he attempts to demonstrate to his courtiers that even a king cannot control nature. According to the legend, he ordered the tide to stop as it was coming in while he was sitting on the beach.
As the waves continued to rise, soaking his feet, he reportedly said something along the lines of, “Let all men know how empty and worthless is the power of kings. For there is none worthy of the name but He whom heaven, earth, and sea obey by eternal laws.” This act was meant to illustrate his humility and recognition of divine authority.
This story has been interpreted in various ways over the centuries, often seen as a lesson in humility and the recognition of human limitations in the face of nature and fate.
King Canute’s legacy is not just about his rule but also about the moral lessons drawn from his actions. It serves as a reminder that no matter how powerful one may be, there are forces beyond control.
Conquest of Northumbria
King Canute’s relationship with Northumbria is a significant aspect of his reign, reflecting both his military strategy and political acumen. Here’s a detailed look at how he conquered Northumbria and what legacy he left behind.
In 1016, during a period of instability in England following the death of King Æthelred the Unready, Canute invaded England. The region of Northumbria was particularly contested, with various factions vying for control.
Canute’s forces, supported by notable Viking leaders like Eiríkr Hákonarson and Thorkell the Tall, launched a successful campaign against the English.
After a series of battles, including the notable Battle of Assandun, Canute and his rival, Edmund Ironside, reached a temporary agreement to divide England. Canute took control of Mercia and Northumbria.
Eric of Hlathir
In 1017, Canute appointed Eric of Hlathir, a Norwegian Viking, as the earl of Northumbria, solidifying his control over the region. This move was strategic, as it helped integrate Viking leadership into the local governance structure.
Eric of Hlathir, also known as Eiríkr Hákonarson, is a fascinating figure in the context of early 11th-century Viking history. Eric was born around 966 AD in Norway. He was the son of Earl Hákon Sigurðarson, a prominent figure in Norwegian history, and he had a notable lineage that connected him to Viking nobility.
He held several important titles, including Earl of Lade and Governor of Norway, before being appointed as the Earl of Northumbria by King Canute in 1017.
Canute’s decision to appoint Eric as the Earl of Northumbria was strategic. It aimed to solidify Viking control over the region and integrate Viking leadership into the existing Anglo-Saxon governance structure. As Earl, Eric was responsible for maintaining order and stability in Northumbria, a region that had seen significant turmoil during the transition of power from Anglo-Saxon to Viking rule.
Contributions and Legacy
- Cultural Integration: Eric played a crucial role in blending Viking and Anglo-Saxon cultures, which helped foster a sense of unity among the diverse populations in Northumbria.
- Military Leadership: His military experience and noble background made him a respected leader, capable of managing both Viking and local interests effectively.
- End of Life: Eric’s life came to an end around 1024 AD in England, marking the conclusion of his significant contributions to the Viking presence in Northumbria.
Eric of Hlathir’s appointment as Earl of Northumbria was a pivotal moment in the Viking Age, showcasing the transition from raiding to governance. His leadership helped stabilize the region and laid the groundwork for future interactions between the Vikings and the Anglo-Saxons.
Important Places in 11th Century Anglo-Saxon Northumberland
- York
- Significance: York was a major political and cultural centre during the Viking Age. It features historical sites such as York Minster and the remnants of the Roman walls.
- Newcastle upon Tyne
- Significance: This city has a vibrant history and is known for its medieval architecture, including the Castle Keep and the Black Gate.
- Bamburgh Castle
- Significance: A historic fortress that has stood for centuries, it was once the capital of the ancient kingdom of Northumbria. The castle offers stunning views of the coastline and is a major tourist attraction.
- Alnwick Castle
- Significance: Known as the seat of the Duke of Northumberland, this castle is famous for its beautiful gardens and as a filming location for the Harry Potter movies. It has a rich history dating back to the 11th century.
- Hadrian’s Wall
- Significance: A UNESCO World Heritage Site, this ancient Roman wall stretches across the north of England and marks the northern limit of the Roman Empire. It offers a glimpse into Roman history and is a popular hiking destination.
- Lindisfarne (Holy Island)
- Significance: Famous for its medieval religious heritage, Lindisfarne is home to the ruins of a 12th-century priory and is known for its beautiful landscapes and tidal causeway.
- Hexham Abbey
- Significance: A historic site with roots dating back to the 7th century, Hexham Abbey is known for its stunning architecture and rich ecclesiastical history.
- Warkworth Castle
- Significance: A well-preserved medieval castle that offers insights into the history of the region and stunning views of the surrounding countryside.
- Tynemouth Priory
- Significance: Tynemouth features a historic priory and castle overlooking the North Sea, with roots tracing back to the early medieval period.
- Ripon
- Significance: An ancient city with roots dating back to the early Christian period. Ripon is known for its historic cathedral, which has been a center of worship since the 7th century. It played a role in the spread of Christianity in the region.
- Knaresborough
- Significance: This market town is famous for its castle and the picturesque setting along the River Nidd. Knaresborough has a rich history, including connections to the medieval period and the development of trade routes.
- Harrogate
- Significance: Known for its spa waters, Harrogate became a popular health resort in the 18th century. Its historical significance lies in its development as a social and cultural hub.
- Selby
- Significance: Located on the River Ouse, Selby was an important trading port and had a significant abbey founded in the 11th century. Its location made it a strategic point for trade and military movements.
- Tadcaster
- Significance: Known for its brewing industry, Tadcaster has historical roots that trace back to Roman times. It was an important settlement in the region, contributing to local trade and economy.
Legacy in Northumbria
Canute’s reign facilitated the blending of Viking and Anglo-Saxon cultures, which had lasting impacts on the region’s identity. This integration helped to foster a sense of unity among the people.
He implemented legal reforms that promoted justice and order, which were crucial for maintaining stability in Northumbria and the broader North Sea Empire.
Canute was a devout Christian and played a significant role in promoting Christianity in Northumbria, which helped align the region with the broader Christian Europe and contributed to its cultural development.
While specific structures from his reign may not be extensively documented, Canute’s influence likely contributed to the establishment of churches and other institutions that reflected the growing Christian presence in Northumbria.
Historic Sources
“The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle”: This primary source chronicles events in England during the Viking Age. It includes references to the political landscape of Northumbria, particularly around the time of Eric’s appointment as Earl. Look for entries around 1016, which detail the power dynamics in the region, including mentions of Newcastle as a significant location during this period.
“Cnut: England’s Viking King” by David A. Hinton: This biography provides insights into King Cnut’s reign and discusses the political significance of various locations in Northumbria, including Newcastle. It highlights how Eric’s governance would have involved managing key cities like Newcastle due to its strategic importance.
“The Northumbrian Kings: A History of the Kingdom of Northumbria” by David Rollason: This book focuses specifically on the history of Northumbria and discusses the rulers, including Eric of Hlathir. It provides context on how Newcastle functioned as a vital trade and military hub during his time, emphasizing its role in the governance of the region.
“The Viking Age: A Reader’s Guide” by Peter Sawyer: This comprehensive overview of the Viking Age discusses the political dynamics in Northumbria, including Eric’s influence. It mentions Newcastle as a key location in the Viking settlement and governance structure.
“The History of the Kings of Britain” by Geoffrey of Monmouth: Although written later, this historical text provides insights into the legendary and historical figures of Britain, including references to Viking leaders and their territories. It discusses the significance of various locations, including Newcastle, in the context of Viking governance.